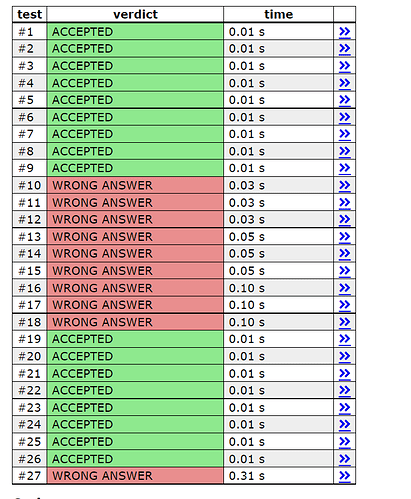
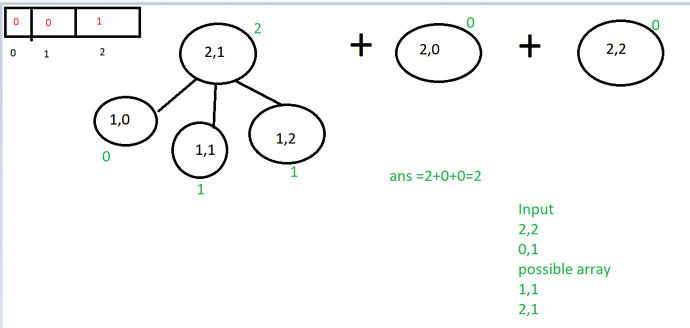
I was trying this question on CSES. Everytime I start dp problem by thinking recursively. I did the same here, but my recursive solution isn’t working and I am not able to figure out why. So it will be very helpful if one can have a look at my code.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long int
#define pb push_back
#define vi vector<int>
#define vb vector<bool>
#define vd vector<double>
#define vc vector<char>
#define vii vector<vi>
#define mp make_pair
#define vpi vector< pair<int, int> >
#define take_input freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin)
#define give_output freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout)
#define fastIO ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);cout.tie(NULL)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mod 1000000007
#define min_pql priority_queue< int, vector<int>, greater<int> >
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
int solve(int n, int m, vi &arr, int i=0) {
if(i == n) return 1;
int cnt=0;
if(arr[i] == 0) {
if(i==0) {
if( i+1<n && arr[i+1]!=0) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; j++){
if( (arr[i+1]+j>=1) && (arr[i+1]+j<=m)) {
arr[i] = arr[i+1]+j;
cnt += solve(n, m, arr, i+1);
arr[i] -= (arr[i+1]+j);
}
}
} else {
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
arr[i] = j;
cnt += solve(n, m, arr, i+1);
arr[i] -= j;
}
}
} else {
set<int> ind;
if(i+1<n && arr[i+1] != 0) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; j++){
ind.insert(arr[i+1]+j);
ind.insert(arr[i-1]+j);
}
} else {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; j++) {
ind.insert(arr[i-1]+j);
}
}
for(int x:ind) {
arr[i] = x;
if(x>=1 && x<=m) cnt += solve(n, m, arr, i+1);
arr[i] -= x;
}
}
} else {
cnt += solve(n, m, arr, i+1);
}
return cnt;
}
int32_t main(){
fastIO;
//take_input;
//give_output;
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
vi arr(n);
for(int &i:arr) cin >> i;
cout << solve(n, m, arr);
}