PROBLEM LINK:
Practice
Div-2 Contest
Div-1 Contest
Author: Vivek Chauhan
Tester: Suchan Park
Editorialist: William Lin
DIFFICULTY:
Easy-Medium
PREREQUISITES:
Sweep Line, Binary Indexed Tree, Segment Tree
PROBLEM:
There are N points, the i-th point is at (i, A_i). For all 0\le i \le N-2, segment i connects points i and i+1. You are given Q queries (l, r, y), meaning that you need to calculate the number of segments in [l, r) that intersect with the horizontal line with height y.
QUICK EXPLANATION:
Segment i will intersect with the line if \min(A_i, A_{i+1})\le y \le \max(A_i, A_{i+1}). We will sweep over y while maintaining the segments that could be intersected in a data structure while answer queries.
EXPLANATION:
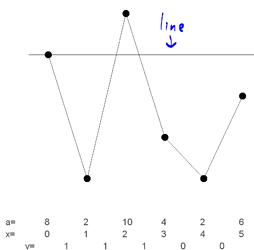
Segment i will be active if it intersects with the horizontal line at y for some query (even if the segment is not within [l, r)). Let the value of a segment be 1 if it is active and 0 if it is inactive. The values of the segments are represented by the array v shown below:
The answer for a query is the number of active segments in [l, r), or the sum of the values of the segments in [l, r). In order to answer the queries efficiently, we will use a sweepline algorithm. The idea of this sweepline algorithm is to imagine a horizontal line sweeping from y=-\infty to y=\infty. At any point in time, the values of the segments should be updated for the current horizontal line. Whenever the horizontal line reaches y_i for some query i, we will answer query i.
There are three types of events:
- For each segment i, when the line reaches y=\min(A_i, A_{i+1}), the value of the segment i will become 1.
- For each query i, when the line reaches y_i, we will answer query i by adding up the values of the segments in [l, r).
- For each segment i, when the line goes over y=\max(A_i, A_{i+1}), the value of the segment i will become 0.
Since the sweepline starts from y=-\infty and moves to y=\infty, we should process the events in increasing order of y. The only thing which remains is to calculate the sum of the values of the segments in [l, r) efficiently for each query. This can be done with any data structure which supports 1. update x_i=v, given i and v 2. find the sum of x_i in a given range. A binary indexed tree or a segment tree will work.
The total time complexity is O(N \log N).
SOLUTIONS:
Setter's Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
typedef int ll;
typedef long double ld;
const ll N = 100005;
char en = '\n';
ll inf = 1e16;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll power(ll x, ll n, ll mod) {
ll res = 1;
x %= mod;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
res = (res * x) % mod;
x = (x * x) % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
struct Event
{
ll type;
ll val;
ll indx;
Event(ll type, ll val, ll indx):type(type), val(val), indx(indx){}
};
bool compMin(const Event &a, const Event &b)
{
if(a.val!=b.val)
return a.val>b.val;
else
return a.type>b.type;
}
bool compMax(const Event &a, const Event &b)
{
if(a.val!=b.val)
return a.val<b.val;
else
return a.type>b.type;
}
// initialise bit to 0
// memset(bit,0,sizeof(bit));
// N>=n
// 1 based indexing
// query - prefix sum
ll bit[N];
void update(ll indx, ll val, ll n) {
while (indx <= n) {
bit[indx] += val;
indx += (indx) & (-indx);
}
}
ll query(ll indx) {
if (indx == 0)
return 0;
ll res = 0;
while (indx >= 1) {
res += bit[indx];
indx -= (indx) & (-indx);
}
return res;
}
ll query(ll a, ll b) { return query(b) - query(a - 1); }
int32_t main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
ll n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
ll arr[n+5];
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>arr[i];
}
ll minPt[n+5],maxPt[n+5];
vector<Event> eventMin;
vector<Event> eventMax;
for(ll i=1;i<n;i++)
{
minPt[i] = min(arr[i], arr[i+1]);
maxPt[i] = max(arr[i], arr[i+1]);
eventMin.emplace_back(1,minPt[i],i);
eventMax.emplace_back(1,maxPt[i],i);
}
ll queries[q+5][3];
for(ll i=1;i<=q;i++) {
ll x1, x2, y;
cin >> x1 >> x2 >> y;
queries[i][0] = x1,queries[i][1]=x2, queries[i][2]= y;
eventMin.emplace_back(2, y, i);
eventMax.emplace_back(2, y, i);
}
sort(eventMin.begin(), eventMin.end(), compMin);
sort(eventMax.begin(), eventMax.end(), compMax);
ll ans[q+5];
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
memset(bit, 0, sizeof(bit));
for(Event& event: eventMin)
{
if(event.type==1)
{
update(event.indx, 1, n-1);
} else
{
ll indx = event.indx;
ans[indx]+=query(queries[indx][0], queries[indx][1]-1);
}
}
memset(bit, 0, sizeof(bit));
for(Event& event: eventMax)
{
if(event.type==1)
{
update(event.indx, 1, n-1);
} else
{
ll indx = event.indx;
ans[indx]+=query(queries[indx][0], queries[indx][1]-1);
}
}
for(ll i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
cout<<(queries[i][1]-queries[i][0])-ans[i]<<en;
}
}
return 0;
}
Tester's Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
const int BUFFER_SIZE = int(1.1e5);
char _buf[BUFFER_SIZE + 10];
int _buf_pos, _buf_len;
char seekChar() {
if(_buf_pos >= _buf_len) {
_buf_len = fread(_buf, 1, BUFFER_SIZE, stdin);
_buf_pos = 0;
}
assert(_buf_pos < _buf_len);
return _buf[_buf_pos];
}
bool seekEof() {
if(_buf_pos >= _buf_len) {
_buf_len = fread(_buf, 1, BUFFER_SIZE, stdin);
_buf_pos = 0;
}
return _buf_pos >= _buf_len;
}
char readChar() {
char ret = seekChar();
_buf_pos++;
return ret;
}
int readInt(int lb, int rb) {
char c = readChar();
int mul = 1;
if(c == '-') {
c = readChar();
mul = -1;
}
assert(isdigit(c));
long long ret = c - '0';
char first_digit = c;
int len = 0;
while(!seekEof() && isdigit(seekChar()) && ++len <= 19) {
ret = ret * 10 + readChar() - '0';
}
ret *= mul;
if(len >= 2) assert(first_digit != '0');
assert(len <= 18);
assert(lb <= ret && ret <= rb);
return (int)ret;
}
void readEoln() {
char c = readChar();
//assert(c == '\n');
assert(c == '\n' || (c == '\r' && readChar() == '\n'));
}
void readSpace() {
assert(readChar() == ' ');
}
struct Event {
int y, x, t;
};
int A[int(1.1e5)];
int ans[int(1.1e5)];
int X1[int(1.1e5)], X2[int(1.1e5)];
int tree[int(1.1e5)];
void add(int x, int v) {
for(; x <= int(1e5); x += x & -x) tree[x] += v;
}
int get(int x) {
int ret = 0;
while(x > 0) {
ret += tree[x];
x &= x-1;
}
return ret;
}
int get(int x, int y) {
return get(y) - get(x-1);
}
void run() {
int N = readInt(2, 100000);
readSpace();
int Q = readInt(1, 100000);
readEoln();
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
A[i] = readInt(1, int(1e9));
if(i + 1 <= N) readSpace(); else readEoln();
}
std::vector<Event> events;
for(int i = 1; i+1 <= N; i++) {
int y1 = std::min(A[i], A[i+1]);
events.push_back({y1, i, +1});
}
std::fill(ans+1, ans+Q+1, 0);
for(int q = 1; q <= Q; q++) {
int x1, x2, y;
x1 = readInt(1, N);
readSpace();
x2 = readInt(1, N);
readSpace();
assert(x1 < x2);
y = readInt(1, int(1e9));
readEoln();
X1[q] = x1;
X2[q] = x2;
events.push_back({y, -1, q});
}
for(int i = 1; i+1 <= N; i++) {
int y2 = std::max(A[i], A[i+1]);
events.push_back({y2, i, -1});
}
std::stable_sort(events.begin(), events.end(), [&](const Event &e1, const Event &e2) { return e1.y < e2.y; });
memset(tree, 0, sizeof tree);
for(const Event &event : events) {
if(event.x > 0) {
add(event.x, event.t);
}else {
ans[event.t] += get(X1[event.t], X2[event.t] - 1);
}
}
for(int q = 1; q <= Q; q++) {
printf("%d\n", ans[q]);
}
}
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
int T = readInt(1, 100);
readEoln();
while(T--) {
run();
}
return 0;
}
Editorialist's Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mxN=1e5;
int n, q, a[mxN], ans[mxN], ql[mxN], qr[mxN], qy[mxN], ft[mxN];
void upd(int i, int x) {
for(++i; i<n; i+=i&-i)
ft[i]+=x;
}
int qry(int i) {
int r=0;
for(; i; i-=i&-i)
r+=ft[i];
return r;
}
struct event {
int y, t, i;
bool operator<(const event &o) const {
return make_pair(y, t)<make_pair(o.y, o.t);
}
};
void solve() {
//input
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
for(int i=0; i<q; ++i)
cin >> ql[i] >> qr[i] >> qy[i], --ql[i], --qr[i];
vector<event> ve;
//create events for the segments
for(int i=0; i+1<n; ++i) {
//add segment
ve.push_back({min(a[i], a[i+1]), 1, i});
//remove segment
ve.push_back({max(a[i], a[i+1]), 3, i});
}
//create events for the queries
for(int i=0; i<q; ++i)
ve.push_back({qy[i], 2, i});
//process events
sort(ve.begin(), ve.end());
for(event e : ve) {
if(e.t==1) {
//add segment
upd(e.i, 1);
} else if(e.t==2) {
//answer query
ans[e.i]=qry(qr[e.i])-qry(ql[e.i]);
} else {
//remove segment
upd(e.i, -1);
}
}
//output
for(int i=0; i<q; ++i)
cout << ans[i] << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
solve();
}
Please give me suggestions if anything is unclear so that I can improve. Thanks ![]()