Editorialist : Sudheera Y S
Problem link : https://www.iarcs.org.in/inoi/2010/zio2010/zio2010-qpaper.pdf
Prerequisites : Logical thinking
Problem Statement :
f(n) = 1 if n = 4
= 3f( ( (2n + 2) mod 11 ) - 1 ) otherwise
g(n) = y mod 10 where
y = 1 if n = 0
= g(n-1) + f( g(n-1) ) + f(n-1) + h(n-1) otherwise
h(n) = x mod 10 where
x = 1 if n = 0
= 2* h(n-1) + g(n-1) + q( f(n-1) mod 10 ) otherwise
q(n) = 1 if n = 7
= f(n) + q(3*n mod 10 ) otherwise
Idea :
We can observe that the function which is easiest to find values is the function f(x) as it only depends on itself and to calculate the value of any function we need to use f(n) ……… we can find function g(n) and h(n) simultaneously and then if we need to find q(n) then we will find it using f(n) and q(n)
We will start filling the table and then we can compute our answers easily ![]()
We will find the values of f(n) only till 7 as we need to find the first 7 values of g and h
f(n) →
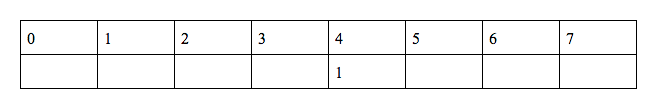
f(4) = 1 … base case
We need to calculate f(n) using f(4)
So … 4 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 5 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 7
f(7) = 3*f(4) = 3 → f(7) = 3
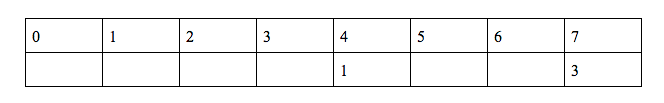
We need to calculate f(n) using f(7)
So … 7 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 8 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 3
f(3) = 3*f(7) = 9 → f(3) = 9

We need to calculate f(n) using f(3)
So … 3 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 4 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 1
f(1) = 3*f(3) = 27 → f(1) = 27

We need to calculate f(n) using f(1)
So … 1 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 2 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 0
f(0) = 3*f(1) = 81 → f(0) = 81

We need to calculate f(n) using f(0)
So … 0 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 1 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 5
f(5) = 3*f(0) = 243 → f(5) = 243
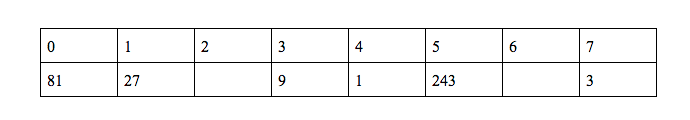
We need to calculate f(n) using f(5)
So … 5 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 6 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 2
f(2) = 3*f(5) = 729 → f(2) = 729
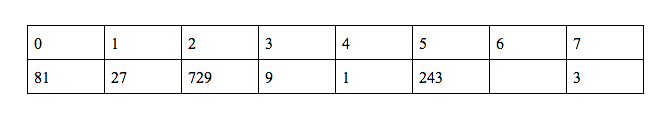
We need to calculate f(n) using f(2)
So … 2 = (2n+2) mod 11 - 1 → 3 = (2n+2) mod 11 → n = 6
f(6) = 3*f(2) = 2187 → f(6) = 2187
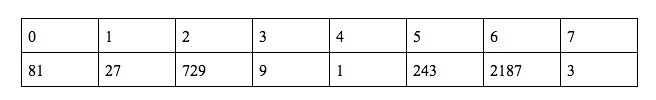
So here we have calculated all the values of f(n) till 7.
Now let us proceed and calculate g(n) and h(n)
g(n) →

h(n) →
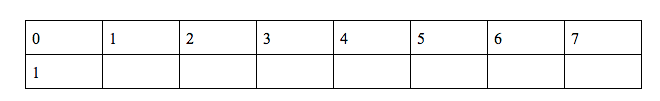
g(0) = 1 …. Base case
h(0) = 1 …. Base case
We need to do g(n) and h(n) simultaneously
g(1) = (g(0) + f(1) + f(0) + h(0)) %10 = (110)%10 = 0
g(n) →
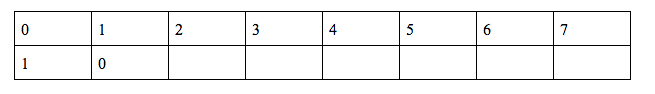
h(1) = (2*h(0) + g(0) + q(1))%10 = (3+q(1))%10
Now we have to calculate q(1) now
q(n) →
To find q(1) we need to find q(3) and to find q(3) we need to find q(9) and to find it we need q(7) which we already know as 1.
So now let us calculate q(9) ……
q(9) = f(9) + q(7) = f(9) + 1 ……
We haven’t found f(9) yet ![]() So let us calculate f(9) in order to find q(9) …
So let us calculate f(9) in order to find q(9) …
To find f(9) we need to know f(8) and we haven’t found f(8) yet ![]() … Let us calculate f(8) …
… Let us calculate f(8) …
To find f(8) we need to know the value of f(6) which is known … So we can calculate f(8) and f(9) ![]()
f(8) = 3*f(6) = 6561
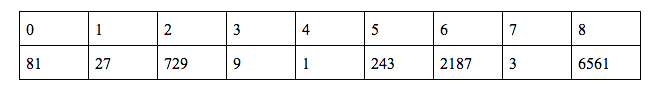
f(9) = 3*f(8) = 19683
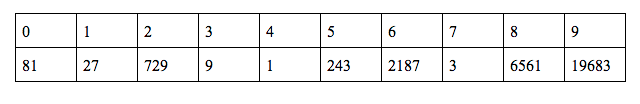
Now we can find q(9)
q(9) = f(9) + q(7) = 19683 + 1 = 19684
q(n) →
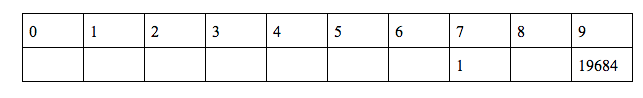
Now we will find q(3)
q(3) = f(3) + q(9) = 9 + 19684 = 19693
q(n) →
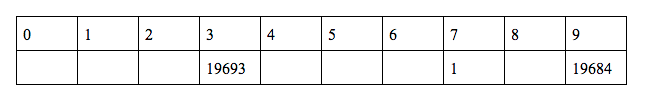
Now we will find q(1)
q(1) = f(1) + q(3) = 27 + 19693 = 19720
q(n) →
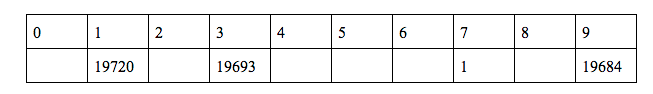
Remember ? we did all of this to calculate h(1) ![]()
h(1) = (2*h(0) + g(0) + q(1))%10 = (19723)%10 = 3
h(n) →
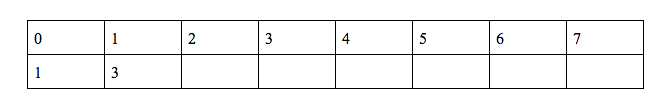
Now we will continue to find the values of g(n) and h(n) till 7
g(2) = (g(1) + f(0) + f(1) + h(1))%10 = 1
g(n) →
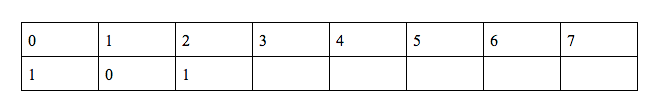
h(2) = (2*h(1) + g(1) + q(7))%10 = 7
h(n) →
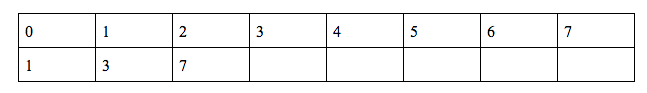
g(3) = (g(2) + f(9) + f(2) + h(2))%10 = 4
g(n) →
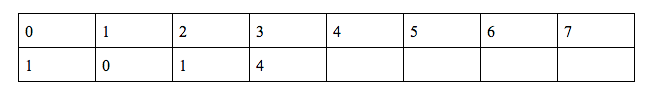
h(3) = (2*h(2) + g(2) + q(9))%10 = 9
h(n) →

g(4) = (g(3) + f(8) + f(3) + h(3))%10 = 3
g(n) →
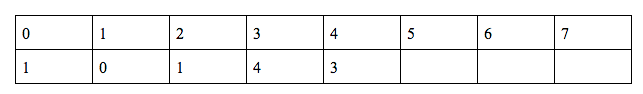
h(4) = (2*h(3) + g(3) + q(9))%10 = 6
h(n) →

g(5) = (g(4) + f(3) + f(4) + h(4))%10 = 9
g(n) →
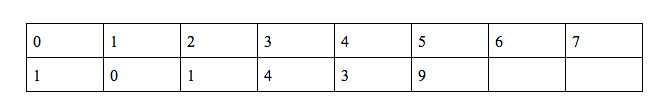
h(5) = (2*h(4) + g(4) + q(1))%10 = 5
h(n) →
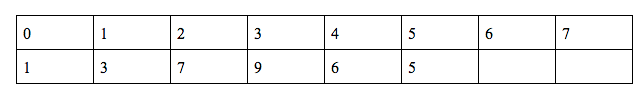
g(6) = (g(5) + f(9) + f(5) + h(5))%10 = 0
g(n) →

h(6) = (2*h(5) + g(5) + q(3))%10 = 2
h(n) →
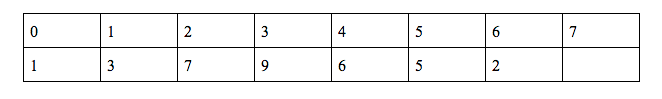
g(7) = (g(6) + f(0) + f(6) + h(6))%10 = 0
g(n) →

Now we have all our answers for all the subtasks , we can stop here ![]()
Subtask A :
Find g(4)
Answer : 3
Subtask B :
Find g(7)
Answer : 0
Subtask C :
Find h(6)
Answer : 2
Code in C++ : ZIO 2010 P3 - Pastebin.com
Hope you understood ![]()