PROBLEM LINK:
Contest Division 1
Contest Division 2
Contest Division 3
Practice
Setter: Aryan Agarwala and Daanish Mahajan
Tester: Aryan
Editorialist: Taranpreet Singh
DIFFICULTY
Easy-Medium
PREREQUISITES
DSU on tree, Euler tour of tree (optionally Auxiliary tree)
PROBLEM
Given a tree with N nodes numbered from 1 to N, answer Q queries of following form.
- Given a set V of K vertices and an integer D, find the number of pairs (u, v) of vertices present in V such that number of edges between simple path from u to v is D
QUICK EXPLANATION
- For each vertex, store the set of queries involving that vertex. We shall answer all queries together in a single dfs on tree
- For each vertex u, store a map containing entries of form ((q, d), c). An entry ((q, d), c) means that from the subset of q-th query, there are c vertices present in subtree of node u and all of them have depth d
- Our DFS shall build the map for the current vertex by copying the map from the child with the largest map size and then brutely updating the map from other children of u.
- Considering tuple ((q, d),c), we can pair all c nodes with the number of nodes in different child of u at depth dep_u + D_q - (d-dep_u) which can be retrieved easily.
EXPLANATION
For this problem, there are two solutions available, one being an offline solution used by the setter and an online solution used by the tester. Both of the solution solve the following simpler problem in same way, but adapt it for original problem differently.
One query containing all vertices
Consider the problem, given a tree with N nodes and an integer D, find the number of pairs of vertices at distance D.
We can solve this problem by running a DFS on the tree, and when processing node w, try to count the number of pairs (u, v) such that the distance between u and v is D and LCA of u and v is w.
We can see that we need
- u and v to be in subtrees of different children of w (Or either u = w or v = w) (To ensure LCA(u, v) = w)
- dep_u + dep_v - 2*dep_w = D
Let’s say, for fixed w, we iterate over all vertices u in the subtree of w. This way, all v are at distance D from u if and only if dep_v = D + 2*dep_w - dep_u holds, and v is in subtree of different child of w.
This is exactly what we are going to do. For each node u, we store a map (d, c) denoting the there are c nodes in subtree of node u which are at depth d.
Implementation
Starting with a map containing only one entry (dep_u, 1) denoting itself at depth dep_u, we consider children of u one by one and merge the maps. This way, after considering all children of u, the map would actually store entries ((q, d), c) representing there are c nodes at depth d which are present in q-th query.
When considering i-th child ch_i, we iterate over the entries (d, c) stored in map of node ch_i. Each of the c nodes at depth d in subtree of ch_i can have distance D with nodes in subtree of first i-1 children of node u, which are at depth D-d + 2*dep_u. Since we process the children one by one, all maps of the first i-1 children are already merged into a map corresponding to node u, so the number of nodes in subtree of first i-1 children of u can be fetched with a single query to map.
But, the above code is currently O(N^2), since each node is processed once for each of its ancestors, which can sum up to N^2 in the case of deep trees.
Optimization
We can notice that we can reuse the map of one child. Instead of building from scratch, let’s pick the child with the largest number of entries on the map, and repeat the process.
With this trick, the time complexity is reduced to O(N*log(N)) since each node needs to be processed for every light ancestor of node (a node is called a light node if it is not the child with the largest subtree when considering its parent). We can prove that there are at most O(log(N)) light ancestors for each node.
Offline solution to Original Problem
We now may have up to 10^5 queries and it is not feasible to run a DFS for each query. So, let’s store all queries and try to answer all queries in a single DFS. Let’s assume D_q denotes the distance given in q-th query, and V_q denotes the set of vertices in q-th query.
We now need to modify our maps, to use pair (q, d) as key and c as value. An entry ((q, d) -> c) in map corresponding to node u represent that in subtree of node u, there are c nodes from V_q at depth d.
The time complexity of the above approach is analogous to the time complexity of the original problem, hence O(N*log(N))
Online Solution
We were able to solve the simpler problem in O(N*log(N)). Let us assume we only need to solve one query, so we can mark nodes in a tree and compute the number of pairs of marked nodes at distance D.
But we need to do this for each query in time complexity in the order of K. A structure called Auxiliary Tree or Virtual Tree comes to our rescue.
For a given subset of K nodes, we can build an edge-weighted tree of at most 2*K-1 nodes from the original tree such that the LCA of any two nodes in this tree is present within this tree. The weight of edges is the distance between their distance in the original tree.
For example, for the tree given in first image, the second denotes the virtual tree for nodes [6,7,8] and the third image denotes tree for subset [3,4,7]
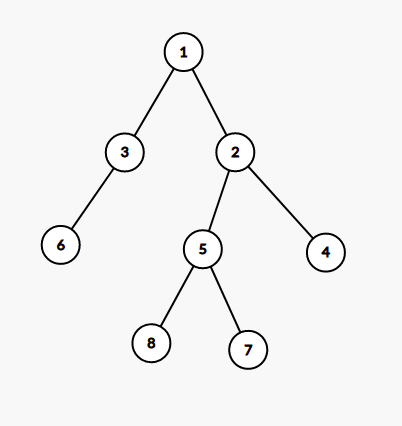
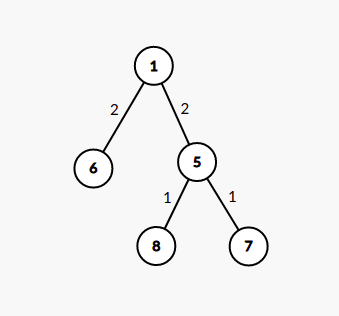
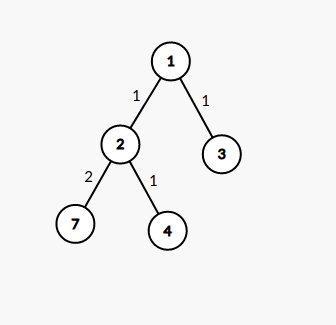
The construction of Auxiliary tree is discussed in several editorials, here, this explaining construction and some others here. A video editorial explaining it in detail can be found here
On this auxiliary tree, the nodes present in queried subset should be considered marked nodes, and now, the depth becomes the distance from the root node. This method solves each query in O(K*log(K)), solving the problem in O(N*log(N)+\sum K*log(K)).
TIME COMPLEXITY
The time complexity is O(N*log(N)+\sum K) with a constant factor, or O(N*log(N) + \sum K*log(K)) per test case.
SOLUTIONS
Setter's Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define initrand mt19937 mt_rand(time(0));
#define rand mt_rand()
#define MOD 1000000007
#define INF 1000000000
#define mid(l, u) ((l+u)/2)
#define rchild(i) (i*2 + 2)
#define lchild(i) (i*2 + 1)
#define lz lazup(l, u, i);
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
long long qans[N];
int qd[N];
vector<int> adj[N];
vector<int> qn[N];
int ind[N];
map<pair<int, int>, int> mp[N];
void dfs(int i, int p, int d){
int bigC = i;
int bigSize = 0;
for(int j: adj[i]){
if(j==p) continue;
dfs(j, i, d+1);
if(mp[ind[j]].size() > bigSize){
bigC = j;
bigSize = mp[ind[j]].size();
}
}
ind[i] = i;
int impind = ind[bigC];
ind[i] = impind;
for(int k: qn[i]){
qans[k] += mp[impind][{qd[k] + d, k}];
}
for(int k: qn[i]){
mp[impind][{d, k}] ++;
}
for(int x: adj[i]){
if(x==p || x==bigC) continue;
for(pair<pair<int, int>, int> k: mp[ind[x]]){
qans[k.first.second] += (((long long) k.second) * ((long long)mp[impind][{qd[k.first.second] + 2*d - k.first.first, k.first.second}]));
}
for(pair<pair<int, int>, int> k: mp[ind[x]]){
mp[impind][k.first] += k.second;
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--) {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){
adj[i].clear();
mp[i].clear();
qn[i].clear();
qans[i] = qd[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
for (int x = 1; x <= q; x++) {
int k, d;
cin >> k >> d;
qd[x] = d;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
int u;
cin >> u;
qn[u].push_back(x);
}
}
dfs(1, 1, 0);
for (int x = 1; x <= q; x++) cout << qans[x] << '\n';
}
}
Tester's Solution
/* in the name of Anton */
/*
Compete against Yourself.
Author - Aryan (@aryanc403)
Atcoder library - https://atcoder.github.io/ac-library/production/document_en/
*/
#ifdef ARYANC403
#include <header.h>
#else
#pragma GCC optimize ("Ofast")
#pragma GCC target ("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4,popcnt,abm,mmx,avx")
//#pragma GCC optimize ("-ffloat-store")
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define dbg(args...) 42;
#endif
using namespace std;
#define fo(i,n) for(i=0;i<(n);++i)
#define repA(i,j,n) for(i=(j);i<=(n);++i)
#define repD(i,j,n) for(i=(j);i>=(n);--i)
#define all(x) begin(x), end(x)
#define sz(x) ((lli)(x).size())
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define X first
#define Y second
#define endl "\n"
typedef long long int lli;
typedef long double mytype;
typedef pair<lli,lli> ii;
typedef vector<ii> vii;
typedef vector<lli> vi;
const auto start_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
void aryanc403()
{
#ifdef ARYANC403
auto end_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = end_time-start_time;
cerr<<"Time Taken : "<<diff.count()<<"\n";
#endif
}
// http://www.open-std.org/jtc1/sc22/wg21/docs/papers/2016/p0200r0.html
template<class Fun> class y_combinator_result {
Fun fun_;
public:
template<class T> explicit y_combinator_result(T &&fun): fun_(std::forward<T>(fun)) {}
template<class ...Args> decltype(auto) operator()(Args &&...args) { return fun_(std::ref(*this), std::forward<Args>(args)...); }
};
template<class Fun> decltype(auto) y_combinator(Fun &&fun) { return y_combinator_result<std::decay_t<Fun>>(std::forward<Fun>(fun)); }
long long readInt(long long l, long long r, char endd) {
long long x=0;
int cnt=0;
int fi=-1;
bool is_neg=false;
while(true) {
char g=getchar();
if(g=='-') {
assert(fi==-1);
is_neg=true;
continue;
}
if('0'<=g&&g<='9') {
x*=10;
x+=g-'0';
if(cnt==0) {
fi=g-'0';
}
cnt++;
assert(fi!=0 || cnt==1);
assert(fi!=0 || is_neg==false);
assert(!(cnt>19 || ( cnt==19 && fi>1) ));
} else if(g==endd) {
if(is_neg) {
x=-x;
}
assert(l<=x&&x<=r);
return x;
} else {
assert(false);
}
}
}
string readString(int l, int r, char endd) {
string ret="";
int cnt=0;
while(true) {
char g=getchar();
assert(g!=-1);
if(g==endd) {
break;
}
cnt++;
ret+=g;
}
assert(l<=cnt&&cnt<=r);
return ret;
}
long long readIntSp(long long l, long long r) {
return readInt(l,r,' ');
}
long long readIntLn(long long l, long long r) {
return readInt(l,r,'\n');
}
string readStringLn(int l, int r) {
return readString(l,r,'\n');
}
string readStringSp(int l, int r) {
return readString(l,r,' ');
}
void readEOF(){
assert(getchar()==EOF);
}
vi readVectorInt(int n,lli l,lli r){
vi a(n);
for(int i=0;i<n-1;++i)
a[i]=readIntSp(l,r);
a[n-1]=readIntLn(l,r);
return a;
}
const lli INF = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFL;
lli seed;
mt19937 rng(seed=chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
inline lli rnd(lli l=0,lli r=INF)
{return uniform_int_distribution<lli>(l,r)(rng);}
class CMP
{public:
bool operator()(ii a , ii b) //For min priority_queue .
{ return ! ( a.X < b.X || ( a.X==b.X && a.Y <= b.Y )); }};
void add( map<lli,lli> &m, lli x,lli cnt=1)
{
auto jt=m.find(x);
if(jt==m.end()) m.insert({x,cnt});
else jt->Y+=cnt;
}
void del( map<lli,lli> &m, lli x,lli cnt=1)
{
auto jt=m.find(x);
if(jt->Y<=cnt) m.erase(jt);
else jt->Y-=cnt;
}
bool cmp(const ii &a,const ii &b)
{
return a.X<b.X||(a.X==b.X&&a.Y<b.Y);
}
const lli mod = 1000000007L;
// const lli maxN = 1000000007L;
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <vector>
namespace atcoder {
struct dsu {
public:
dsu() : _n(0) {}
explicit dsu(int n) : _n(n), parent_or_size(n, -1) {}
int merge(int a, int b) {
assert(0 <= a && a < _n);
assert(0 <= b && b < _n);
int x = leader(a), y = leader(b);
if (x == y) return x;
if (-parent_or_size[x] < -parent_or_size[y]) std::swap(x, y);
parent_or_size[x] += parent_or_size[y];
parent_or_size[y] = x;
return x;
}
bool same(int a, int b) {
assert(0 <= a && a < _n);
assert(0 <= b && b < _n);
return leader(a) == leader(b);
}
int leader(int a) {
assert(0 <= a && a < _n);
if (parent_or_size[a] < 0) return a;
return parent_or_size[a] = leader(parent_or_size[a]);
}
int size(int a) {
assert(0 <= a && a < _n);
return -parent_or_size[leader(a)];
}
std::vector<std::vector<int>> groups() {
std::vector<int> leader_buf(_n), group_size(_n);
for (int i = 0; i < _n; i++) {
leader_buf[i] = leader(i);
group_size[leader_buf[i]]++;
}
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result(_n);
for (int i = 0; i < _n; i++) {
result[i].reserve(group_size[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < _n; i++) {
result[leader_buf[i]].push_back(i);
}
result.erase(
std::remove_if(result.begin(), result.end(),
[&](const std::vector<int>& v) { return v.empty(); }),
result.end());
return result;
}
private:
int _n;
std::vector<int> parent_or_size;
};
} // namespace atcoder
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i < (b); ++i)
#define trav(a, x) for(auto& a : x)
// #define all(x) begin(x), end(x)
// #define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
// typedef vector<int> vi;
typedef vector<pii> vpi;
typedef vector<vpi> graph;
graph readTree(lli n){
graph e(n);
atcoder::dsu d(n);
for(lli i=1;i<n;++i){
const lli u=readIntSp(1,n)-1;
const lli v=readIntLn(1,n)-1;
e[u].pb({v,1});
e[v].pb({u,1});
d.merge(u,v);
}
assert(d.size(0)==n);
return e;
}
template<class T>
struct RMQ {
vector<vector<T>> jmp;
RMQ(const vector<T>& V) {
int N = sz(V), on = 1, depth = 1;
while (on < N) on *= 2, depth++;
jmp.assign(depth, V);
rep(i,0,depth-1) rep(j,0,N)
jmp[i+1][j] = min(jmp[i][j],
jmp[i][min(N - 1, j + (1 << i))]);
}
T query(int a, int b) {
assert(a < b); // or return inf if a == b
int dep = 31 - __builtin_clz(b - a);
return min(jmp[dep][a], jmp[dep][b - (1 << dep)]);
}
};
struct LCA {
vi time;
vector<ll> dist;
RMQ<pii> rmq;
LCA(graph& C) : time(sz(C), -99), dist(sz(C)), rmq(dfs(C)) {}
vpi dfs(graph& C) {
vector<tuple<int, int, int, ll>> q(1);
vpi ret;
int T = 0, v, p, d; ll di;
while (!q.empty()) {
tie(v, p, d, di) = q.back();
q.pop_back();
if (d) ret.emplace_back(d, p);
time[v] = T++;
dist[v] = di;
trav(e, C[v]) if (e.first != p)
q.emplace_back(e.first, v, d+1, di + e.second);
}
return ret;
}
int query(int a, int b) {
if (a == b) return a;
a = time[a], b = time[b];
return rmq.query(min(a, b), max(a, b)).second;
}
ll distance(int a, int b) {
int lca = query(a, b);
return dist[a] + dist[b] - 2 * dist[lca];
}
};
vpi compressTree(LCA& lca, const vi& subset) {
static vi rev; rev.resize(sz(lca.dist));
vi li = subset, &T = lca.time;
auto cmp = [&](int a, int b) { return T[a] < T[b]; };
sort(all(li), cmp);
int m = sz(li)-1;
rep(i,0,m) {
int a = li[i], b = li[i+1];
li.push_back(lca.query(a, b));
}
sort(all(li), cmp);
li.erase(unique(all(li)), li.end());
rep(i,0,sz(li)) rev[li[i]] = i;
vpi ret = {pii(0, li[0])};
rep(i,0,sz(li)-1) {
int a = li[i], b = li[i+1];
ret.emplace_back(lca.query(a, b), b);
}
return ret;
}
//cities will be changed to new ids.
graph init(LCA& lca,vi &cities)
{
graph ee;
auto subset=cities;
sort(all(subset));
subset.erase(unique(all(subset)),subset.end());
auto ctree=compressTree(lca,subset);
subset.clear();
for(auto x:ctree)
{
subset.pb(x.X);
subset.pb(x.Y);
}
sort(all(subset));
subset.erase(unique(all(subset)),subset.end());
const lli n=sz(subset);
ee.clear();ee.resize(n);
auto gt=[&](const lli x){
return lower_bound(all(subset),x)-subset.begin();
};
for(auto x:ctree)
{
if(x.X==x.Y)
continue;
const lli u=gt(x.X);
const lli v=gt(x.Y);
const lli d=lca.distance(x.X,x.Y);
ee[u].pb({v,d});
ee[v].pb({u,d});
}
for(auto &x:cities)
x=gt(x);
return ee;
}
lli ans;
vi f;
lli dd;
void dfs(const graph &e,lli u,lli p,lli h,map<lli,lli> &a){
if(f[u]){
a[h]+=f[u];
ans+=f[u]*(f[u]-1);
}
for(auto x:e[u]){
if(x.X==p)
continue;
map<lli,lli> b;
dfs(e,x.X,u,h+x.Y,b);
if(sz(b)>sz(a))
a.swap(b);
for(auto x:b){
auto it=a.find(dd+2*h-x.X);
if(it==a.end())
continue;
ans+=x.Y*(it->Y);
}
for(auto x:b)
a[x.X]+=x.Y;
}
}
void solve(const graph &e,const vi &a,const lli d){
const lli n=sz(e);
f.clear();f.resize(n);
for(auto x:a)
f[x]++;
ans=0;
map<lli,lli> b;
dd=d;
dfs(e,0,-1,0,b);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main(void) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);
// freopen("txt.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("txt.out", "w", stdout);
// cout<<std::fixed<<std::setprecision(35);
lli T=readIntLn(1,5);
while(T--)
{
const lli n=readIntSp(1,1e5);
lli q=readIntLn(1,1e5);
auto e=readTree(n);
lli sumK=0;
LCA lca(e);
while(q--){
const lli k=readIntSp(1,1e5);
const lli d=readIntSp(0,1e5);
auto a = readVectorInt(k,1,n);
sumK+=k;
for(auto &x:a)
x--;
graph ee;
ee=init(lca,a);
solve(ee,a,d);
}
assert(sumK<=1e5);
} aryanc403();
readEOF();
return 0;
}
Editorialist's Offline Solution
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class PAIRCNT{
//SOLUTION BEGIN
int[][] tree;
int[] dep, st, en, eu;
int time;
List<Integer>[] inc;
int[] D;
long[] ans;
TreeMap<Pair, Integer>[] count;
void pre() throws Exception{}
void solve(int TC) throws Exception{
int N = ni(), Q = ni();
int[] from = new int[N-1], to = new int[N-1];
for(int i = 0; i< N-1; i++){
from[i] = ni()-1;
to[i] = ni()-1;
}
tree = tree(N, from, to);
inc = new ArrayList[N];
for(int i = 0; i< N; i++)inc[i] = new ArrayList<>();
D = new int[Q];
for(int q = 0; q< Q; q++){
int K = ni();
D[q] = ni();
int[] V = new int[K];
for(int i = 0; i< K; i++){
V[i] = ni()-1;
inc[V[i]].add(q);
}
}
count = new TreeMap[N];
ans = new long[Q];
dep = new int[N];
st = new int[N];
en = new int[N];
eu = new int[N];
time = -1;
pre(0, -1);
dfs(0, -1);
for(int q = 0; q< Q; q++)pn(ans[q]);
}
void pre(int u, int p){
eu[++time] = u;
st[u] = time;
for(int v:tree[u]){
if(v == p)continue;
dep[v] = dep[u]+1;
pre(v, u);
}
en[u] = time;
}
void dfs(int u, int p){
for(int v:tree[u])if(v != p)dfs(v, u);
int hc = -1;
for(int v:tree[u])if(v != p && (hc == -1 || count[v].size() > count[hc].size()))hc = v;
if(hc != -1)count[u] = count[hc];
else count[u] = new TreeMap<>();
for(int qid: inc[u]){
ans[qid] += count[u].getOrDefault(new Pair(qid, dep[u]+D[qid]), 0);
count[u].put(new Pair(qid, dep[u]), count[u].getOrDefault(new Pair(qid, dep[u]), 0)+1);
}
for(int v:tree[u]){
if(v == p || v == hc)continue;
count[v].entrySet().forEach(e -> {
Pair pair = e.getKey();
int qid = pair.qid, de = pair.dep, freq = e.getValue();
if(de-dep[u] <= D[qid]){
int dep2 = dep[u]+D[qid]-(de-dep[u]);
ans[qid] += freq*(long)count[u].getOrDefault(new Pair(qid, dep2), 0);
}
});
count[v].entrySet().forEach(e -> {
Pair pair = e.getKey();
int freq = e.getValue();
count[u].put(pair, count[u].getOrDefault(pair, 0)+freq);
});
}
}
int[][] tree(int N, int[] from, int[] to){
int[] cnt = new int[N];
for(int x:from)cnt[x]++;
for(int x:to)cnt[x]++;
int[][] g = new int[N][];
for(int i = 0; i< N; i++)g[i] = new int[cnt[i]];
for(int i = 0; i< N-1; i++){
g[from[i]][--cnt[from[i]]] = to[i];
g[to[i]][--cnt[to[i]]] = from[i];
}
return g;
}
class Pair implements Comparable<Pair>{
int qid, dep;
//Number of nodes of query id qid, at depth dep are stored in count;
public Pair(int q, int d){
qid = q;
dep = d;
}
public int compareTo(Pair p){
if(qid != p.qid)return Integer.compare(qid, p.qid);
return Integer.compare(dep, p.dep);
}
}
//SOLUTION END
void hold(boolean b)throws Exception{if(!b)throw new Exception("Hold right there, Sparky!");}
static boolean multipleTC = true;
FastReader in;PrintWriter out;
void run() throws Exception{
in = new FastReader();
out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
//Solution Credits: Taranpreet Singh
int T = (multipleTC)?ni():1;
pre();for(int t = 1; t<= T; t++)solve(t);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
new PAIRCNT().run();
}
int bit(long n){return (n==0)?0:(1+bit(n&(n-1)));}
void p(Object o){out.print(o);}
void pn(Object o){out.println(o);}
void pni(Object o){out.println(o);out.flush();}
String n()throws Exception{return in.next();}
String nln()throws Exception{return in.nextLine();}
int ni()throws Exception{return Integer.parseInt(in.next());}
long nl()throws Exception{return Long.parseLong(in.next());}
double nd()throws Exception{return Double.parseDouble(in.next());}
class FastReader{
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader(){
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public FastReader(String s) throws Exception{
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s));
}
String next() throws Exception{
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()){
try{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
}catch (IOException e){
throw new Exception(e.toString());
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
String nextLine() throws Exception{
String str = "";
try{
str = br.readLine();
}catch (IOException e){
throw new Exception(e.toString());
}
return str;
}
}
}
Editorialist's Online Solution
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class PAIRCNT{
//SOLUTION BEGIN
void pre() throws Exception{}
void solve(int TC) throws Exception{
int N = ni(), Q = ni();
int[] from = new int[N-1], to = new int[N-1];
for(int i = 0; i< N-1; i++){
from[i] = ni()-1;
to[i] = ni()-1;
}
int[][] tree = tree(N, from, to);
LCA lcaFinder = new LCA(tree);
int[] depth = new int[N], st = new int[N], en = new int[N];
time = -1;
pre(tree, depth, st, en, 0, -1);
freq = new int[N];
for(int q = 0; q< Q; q++){
int K = ni(), D = ni();
Integer[] V = new Integer[K];
for(int i = 0; i< K; i++)V[i] = ni()-1;
int[][][] auxTree = buildAuxTree(tree, lcaFinder, depth, st, en, V);
pn(countPairs(auxTree, K, D));
}
}
int[] freq;
long countPairs(int[][][] tree, int K, int D){
int N = tree.length;
int[] sub = new int[N], dep = new int[N];
sub(tree, sub, dep, 0, -1);
HashMap<Integer, Integer>[] map = new HashMap[N];
return dfs(tree, K, D, map, sub, dep, 0, -1);
}
void sub(int[][][] tree, int[] sub, int[] dep, int u, int p){
sub[u] = 1;
for(int[] v:tree[u]){
if(v[0] == p)continue;
dep[v[0]] = dep[u]+v[1];
sub(tree, sub, dep, v[0], u);
sub[u] += sub[v[0]];
}
}
long dfs(int[][][] tree, int K, int D, HashMap<Integer, Integer>[] map, int[] sub, int[] dep, int u, int p){
int hc = -1;
long ans = 0;
for(int[] v:tree[u])
if(v[0] != p && (hc == -1 || sub[v[0]] > sub[hc]))
hc = v[0];
for(int[] v:tree[u])
if(v[0] != p && v[0] != hc)
ans += dfs(tree, K, D, map, sub, dep, v[0], u);
if(hc != -1){
ans += dfs(tree, K, D, map, sub, dep, hc, u);
map[u] = map[hc];
}else{
map[u] = new HashMap<>();
}
if(u < K){
ans += map[u].getOrDefault(dep[u]+D, 0);
map[u].put(dep[u], map[u].getOrDefault(dep[u], 0)+1);
}
for(int[] v:tree[u]){
if(v[0] == p || v[0] == hc)continue;
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> e:map[v[0]].entrySet()){
int d = e.getKey(), f = e.getValue();
if(d-dep[u] <= D){
int pairDep = dep[u] + (D-(d-dep[u]));
ans += f*(long)map[u].getOrDefault(pairDep, 0);
}
}
map[v[0]].entrySet().forEach(e -> {
map[u].put(e.getKey(), map[u].getOrDefault(e.getKey(), 0)+e.getValue());
});
}
return ans;
}
int[][][] buildAuxTree(int[][] tree, LCA lca, int[] dep, int[] st, int[] en, Integer[] V){
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
int c = 0;
for(Integer x:V)map.put(x, c++);
Arrays.sort(V, (Integer i1, Integer i2) -> Integer.compare(st[i1], st[i2]));//Sorted by euler in time
for(int i = 1; i< V.length; i++){
int w = lca.lca(V[i-1], V[i]);
if(!map.containsKey(w))map.put(w, c++);
}
//The set of vertices to be present in aux Tree is ready. Now let's add edges between them
//We also relabel nodes from 0 to SZ-1, where labels from 0 to K-1 are initial labels
int SZ = c;
int[] from = new int[SZ-1], to = new int[SZ-1], w = new int[SZ-1];
int cnt = 0;
Integer[] vertices = map.keySet().toArray(new Integer[SZ]);
Arrays.sort(vertices, (Integer i1, Integer i2) -> Integer.compare(dep[i2], dep[i1]));//sorting by depth in descending order
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> tin = new TreeMap<>();//Contains pair (tin[u], u) for vertices u which are processed, and whose parents are not yet assigned
for(int u:vertices){
//Processing vertex u, all deeper vertices already processed
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> e;
//Following loop runs over all vertices v such that st[u] <= st[v] && en[v] <= en[u]
while((e = tin.ceilingEntry(st[u])) != null && en[e.getValue()] <= en[u]){
int v = e.getValue();
//add edge u -> v with weight dist(u, v)
from[cnt] = map.get(u);
to[cnt] = map.get(v);
w[cnt] = dep[v]-dep[u];
cnt++;
tin.remove(e.getKey());
}
tin.put(st[u], u);
}
return weightedTree(SZ, from, to, w);
}
int time;
void pre(int[][] tree, int[] dep, int[] st, int[] en, int u, int p){
st[u] = ++time;
for(int v:tree[u])if(v != p){
dep[v] = dep[u]+1;
pre(tree, dep, st, en, v, u);
}
en[u] = time;
}
int[][][] weightedTree(int N, int[] from, int[] to, int[] w){
int[] cnt = new int[N];
for(int x:from)cnt[x]++;
for(int x:to)cnt[x]++;
int[][][] g = new int[N][][];
for(int i = 0; i< N; i++)g[i] = new int[cnt[i]][];
for(int i = 0; i< N-1; i++){
g[from[i]][--cnt[from[i]]] = new int[]{to[i], w[i]};
g[to[i]][--cnt[to[i]]] = new int[]{from[i], w[i]};
}
return g;
}
int[][] tree(int N, int[] from, int[] to){
int[] cnt = new int[N];
for(int x:from)cnt[x]++;
for(int x:to)cnt[x]++;
int[][] g = new int[N][];
for(int i = 0; i< N; i++)g[i] = new int[cnt[i]];
for(int i = 0; i< N-1; i++){
g[from[i]][--cnt[from[i]]] = to[i];
g[to[i]][--cnt[to[i]]] = from[i];
}
return g;
}
class LCA{
int n = 0, ti= -1;
int[] eu, fi, d;
RMQ rmq;
public LCA(int[][] g){
n = g.length;
eu = new int[2*n-1];fi = new int[n];d = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(fi, -1);Arrays.fill(eu, -1);
dfs(g, 0, -1);
rmq = new RMQ(eu, d);
}
public LCA(int[] eu, int[] fi, int[] d){
this.n = eu.length;
this.eu = eu;
this.fi = fi;
this.d = d;
rmq = new RMQ(eu, d);
}
void dfs(int[][] g, int u, int p){
eu[++ti] = u;fi[u] = ti;
for(int v:g[u])if(v!=p){
d[v] = d[u]+1;
dfs(g, v, u);eu[++ti] = u;
}
}
int lca(int u, int v){return rmq.query(Math.min(fi[u], fi[v]), Math.max(fi[u], fi[v]));}
int dist(int u, int v){return d[u]+d[v]-2*d[lca(u,v)];}
class RMQ{
int[] len, d;
int[][] rmq;
public RMQ(int[] ar, int[] weight){
len = new int[ar.length+1];
this.d = weight;
for(int i = 2; i<= ar.length; i++)len[i] = len[i>>1]+1;
rmq = new int[len[ar.length]+1][ar.length];
for(int i = 0; i< rmq.length; i++)
for(int j = 0; j< rmq[i].length; j++)
rmq[i][j] = -1;
for(int i = 0; i< ar.length; i++)rmq[0][i] = ar[i];
for(int b = 1; b<= len[ar.length]; b++)
for(int i = 0; i + (1<<b)-1< ar.length; i++)
if(weight[rmq[b-1][i]]<weight[rmq[b-1][i+(1<<(b-1))]])rmq[b][i] =rmq[b-1][i];
else rmq[b][i] = rmq[b-1][i+(1<<(b-1))];
}
int query(int l, int r){
if(l==r)return rmq[0][l];
int b = len[r-l];
if(d[rmq[b][l]]<d[rmq[b][r-(1<<b)]])return rmq[b][l];
return rmq[b][r-(1<<b)];
}
}
}
//SOLUTION END
void hold(boolean b)throws Exception{if(!b)throw new Exception("Hold right there, Sparky!");}
static boolean multipleTC = true;
FastReader in;PrintWriter out;
void run() throws Exception{
in = new FastReader();
out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
//Solution Credits: Taranpreet Singh
int T = (multipleTC)?ni():1;
pre();for(int t = 1; t<= T; t++)solve(t);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
new PAIRCNT().run();
}
int bit(long n){return (n==0)?0:(1+bit(n&(n-1)));}
void p(Object o){out.print(o);}
void pn(Object o){out.println(o);}
void pni(Object o){out.println(o);out.flush();}
String n()throws Exception{return in.next();}
String nln()throws Exception{return in.nextLine();}
int ni()throws Exception{return Integer.parseInt(in.next());}
long nl()throws Exception{return Long.parseLong(in.next());}
double nd()throws Exception{return Double.parseDouble(in.next());}
class FastReader{
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader(){
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public FastReader(String s) throws Exception{
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s));
}
String next() throws Exception{
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()){
try{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
}catch (IOException e){
throw new Exception(e.toString());
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
String nextLine() throws Exception{
String str = "";
try{
str = br.readLine();
}catch (IOException e){
throw new Exception(e.toString());
}
return str;
}
}
}
Feel free to share your approach. Suggestions are welcomed as always. ![]()
 .
.